Till now the sorting architectures discussed are based on the accessing of data elements in parallel. In real time situation the data streams are serial and serial to parallel conversion is costly as well as time consuming. On the other hand, parallel sorting architectures are very costly in terms of comparators. Thus alternate sorting architectures should be adopted in case of huge data stream. Here, we will discuss a sorting processor which is based on the insertion sort technique and works on a serial stream of ![]() data words.
data words.
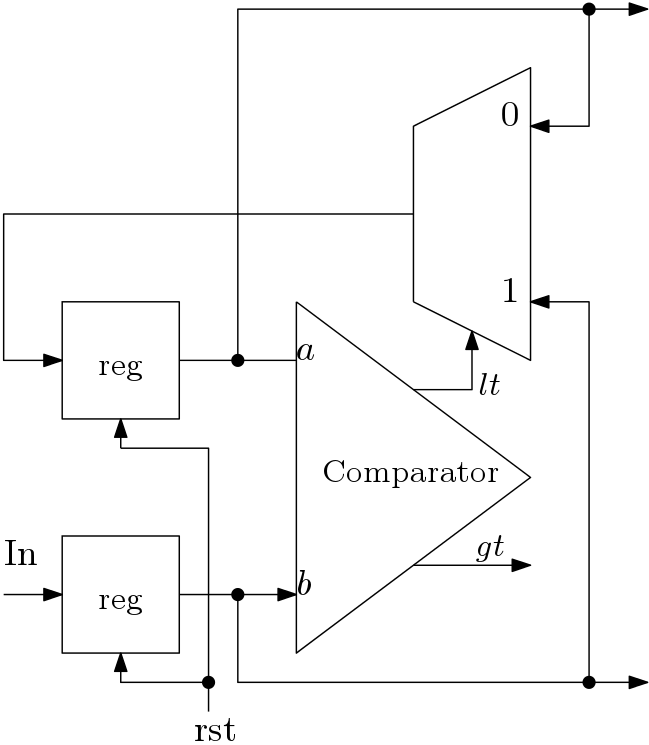
In insertion sort technique, values from the unsorted part is inserted at the correct position of the sorted part. Two data elements are sorted in similar way as it was done previously but the BN block is different from the BN block discussed in previous tutorials. Architecture of this BN block is shown in Figure 1. Maximum of two elements is stored in a register and again fed to the comparator. One ![]() signal is there to clear the contents of the registers as per requirement.
signal is there to clear the contents of the registers as per requirement.
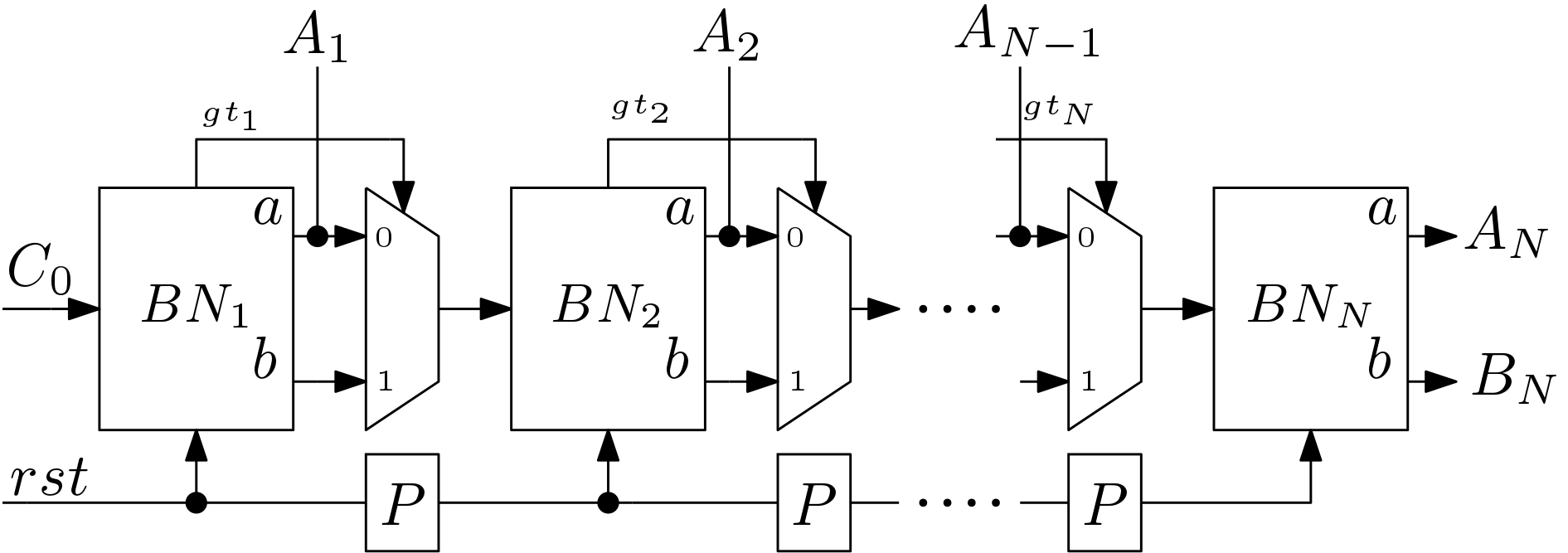
Insertion sorting algorithm based sorting network to sort ![]() data elements is shown in Figure 2. Here,
data elements is shown in Figure 2. Here, ![]() number of BN blocks are used. Serial data is fed to the
number of BN blocks are used. Serial data is fed to the ![]() pin. The
pin. The ![]() block sorts two data and maximum of them is
block sorts two data and maximum of them is ![]() . The minimum value from the
. The minimum value from the ![]() block is passed to the next block through a MUX. If a data greater than the present value of
block is passed to the next block through a MUX. If a data greater than the present value of ![]() occurs at input of
occurs at input of ![]() then this value will be assigned to
then this value will be assigned to ![]() and the past value of
and the past value of ![]() is passed to the next BN block. Similar operation is carried out for the other BN blocks. After the
is passed to the next BN block. Similar operation is carried out for the other BN blocks. After the ![]() clock cycles
clock cycles ![]() holds the maximum of
holds the maximum of ![]() data elements. Similarly values of
data elements. Similarly values of ![]() ,
, ![]() , … ,
, … , ![]() are evaluated. The Sorting Network-N block takes
are evaluated. The Sorting Network-N block takes ![]() clock cycles to sort
clock cycles to sort ![]() data elements.
data elements.
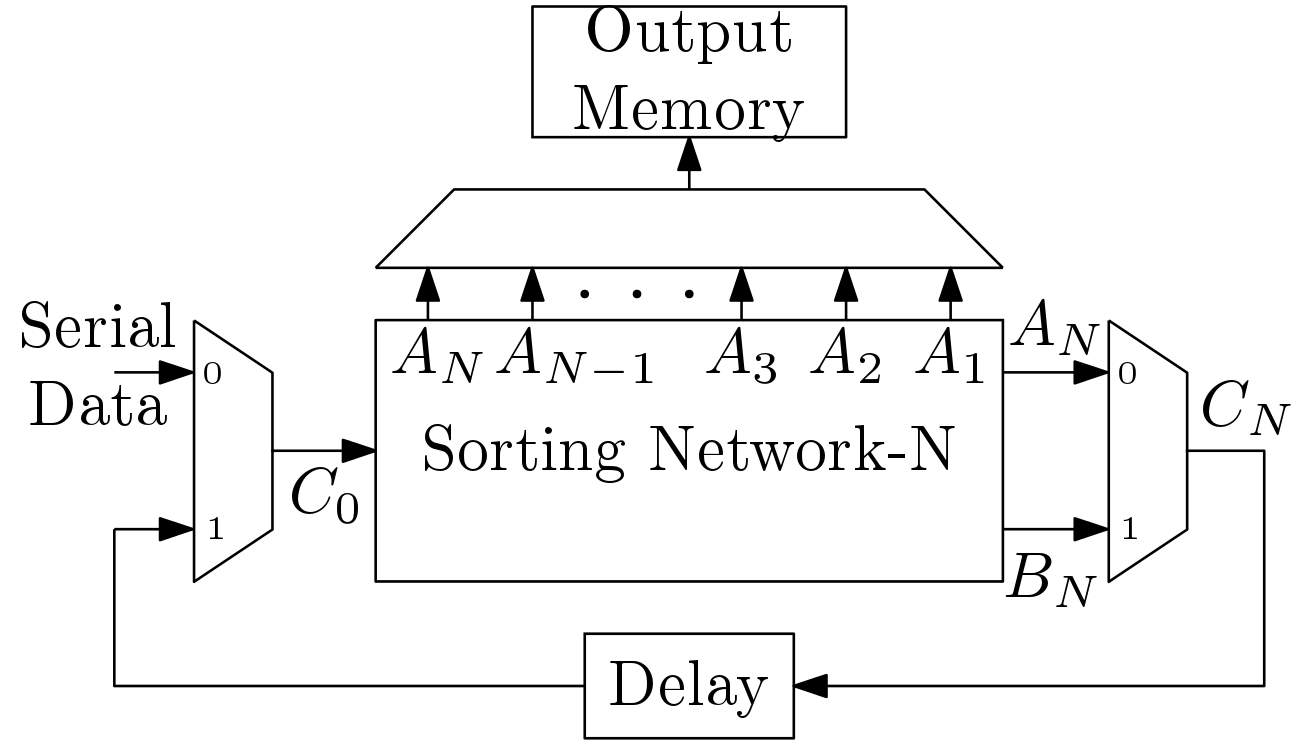
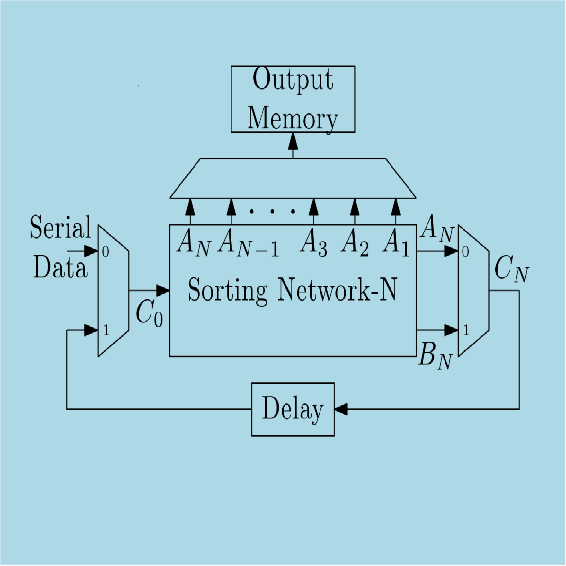
The next job is to sort the ![]() elements. The sorting processor architecture is built using the Sorting Network-N block and is shown in Figure 3. The sorted elements can be stored in an output memory through a MUX unit. Here, unsorted elements are again fed to the Sorting Network-N through the
elements. The sorting processor architecture is built using the Sorting Network-N block and is shown in Figure 3. The sorted elements can be stored in an output memory through a MUX unit. Here, unsorted elements are again fed to the Sorting Network-N through the ![]() net. The unsorted elements are again sorted serially using the same block. After
net. The unsorted elements are again sorted serially using the same block. After ![]() clock cycles
clock cycles ![]() holds the maximum value of the unsorted part. This way the whole array of
holds the maximum value of the unsorted part. This way the whole array of ![]() words is sorted.
words is sorted.
This sorting processor sorts a serial array of data elements and results sorted array array of ![]() elements at a time. Apart from the MUX and registers, the sorting processor mainly consists of
elements at a time. Apart from the MUX and registers, the sorting processor mainly consists of ![]() BN blocks. If the value of
BN blocks. If the value of ![]() is to be increased, the number of BN blocks will increase. The timing complexity of this sort processor can be estimated by expressing
is to be increased, the number of BN blocks will increase. The timing complexity of this sort processor can be estimated by expressing ![]() in terms of
in terms of ![]() as
as ![]() . Then total timing complexity will be
. Then total timing complexity will be ![]() . If the value of
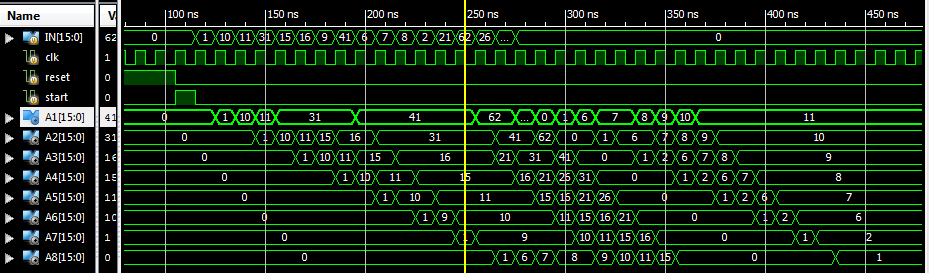
. If the value of ![]() is 8 then total time to sort 32 data elements will be 88 number of clock cycles. This is obviously higher than the processing time of the parallel sorting processors but this sorting processor is hardware efficient. The XILINX output of this sorting processor is shown in Figure 4.
is 8 then total time to sort 32 data elements will be 88 number of clock cycles. This is obviously higher than the processing time of the parallel sorting processors but this sorting processor is hardware efficient. The XILINX output of this sorting processor is shown in Figure 4.
Verilog Code of Sorting Processor to Sort N Words
Sorting processor is very important in implementing any signal processing or image processing algorithms. This is a Verilog code of a sorting processor which sorts a serial data stream. This is a prototype design to sort 32 data elements but can used to sort serial data stream of any length.
